Meta tags are pieces of code that provide instructions to search engines on how to display your website. Moreover, they instruct browsers on how to present the information to users.
Meta tags are part of every webpage, although visitors can only see them in the source code. SEO with meta tags is important to know, it can boost ranking and help with click through rates and lower bounce rates.
This tutorial will teach you the ins and outs of the six most crucial meta tags for search engine optimization.
- Meta Title
- Meta Description
- Meta robots
- Meta-refresh redirect
- Charset meta
- Meta viewport
Meta title
What you see below is the title that will appear in Google and other search engine results.
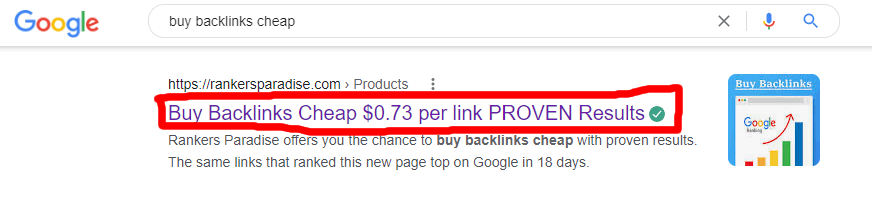 SIDENOTE. The title tag doesn’t always appear in Google search results. Different things are shown at other times.
SIDENOTE. The title tag doesn’t always appear in Google search results. Different things are shown at other times.
Just how crucial it is for search engine optimization
In the words of Google
Titles play a crucial role in providing consumers with an immediate understanding of a result’s content and relevance to their query. It’s crucial to have high-quality titles on your web pages, since they are frequently the only piece of information needed to pick which result to click on.
Most effective methods
- Put a different title tag on each page you create;
- Try to be succinct while yet elucidating the main points;
- Titles should be specific and descriptive, not generic;
- Capitalize sentences and titles;
- Make something interesting enough to click on (but not clickbait);
- Respond according to the user’s search intent;
- Always use your keyword where it makes sense;
- Please limit your response to 60 characters or less.
Tips for creating a title tag
In the head section of your website, copy the following code:

An SEO plugin, such as Yoast, is a must-have if you’re using WordPress. When editing a page or post, look for a field where you may provide the title tag.
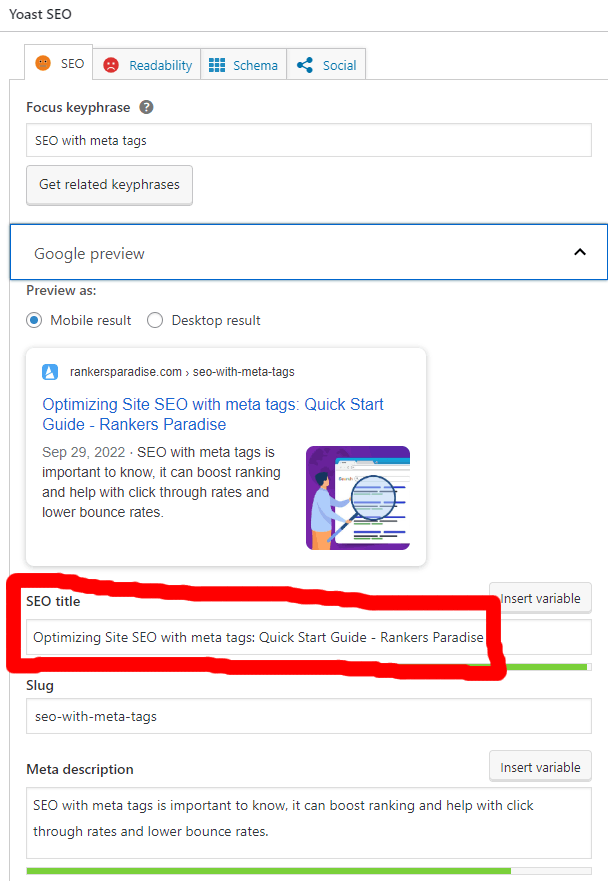
Similar features may be found pre-implemented in other content management systems like Weebly and Strikingly.
Methods for identifying and correcting title tag errors
In general, title tags have four problems:
- Inappropriate length. Google recommends keeping titles “descriptive and simple” and “avoiding unduly lengthy or verbose titles.”
- Cannot be found. Google recommends using a title tag on every page.
- There are a number of title tags on this page. If a page has more than one title tag, certain search engines may choose to show the wrong one.
- There are several instances of duplicate page titles. It is recommended by Google that you “have unique, descriptive titles for each page on your site.”
You may use a free tool like SERPSim to examine a page for the first two problems.
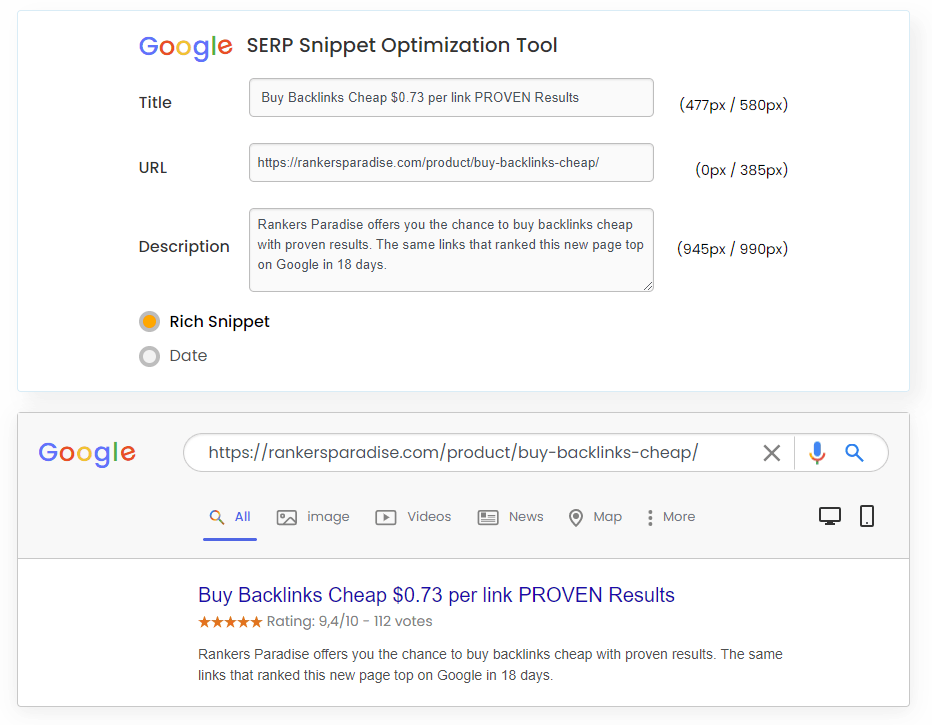
If it doesn’t bring up a title, you’ll have to give it one.
If the number of red pixels increases, the length of the title tag must be reduced.
Crawling your site using Ahrefs’ Site Audit will check for numerous title tags and duplicates.
From there, look for “Multiple title tag” issues in the On page report:
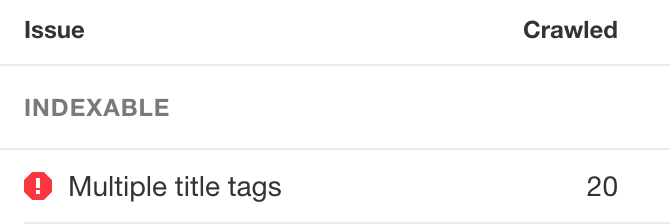
You may fix this by omitting one of the tags from the impacted pages.
Find any title tags that have “Bad duplicate” issues by going to the Duplicate content report:
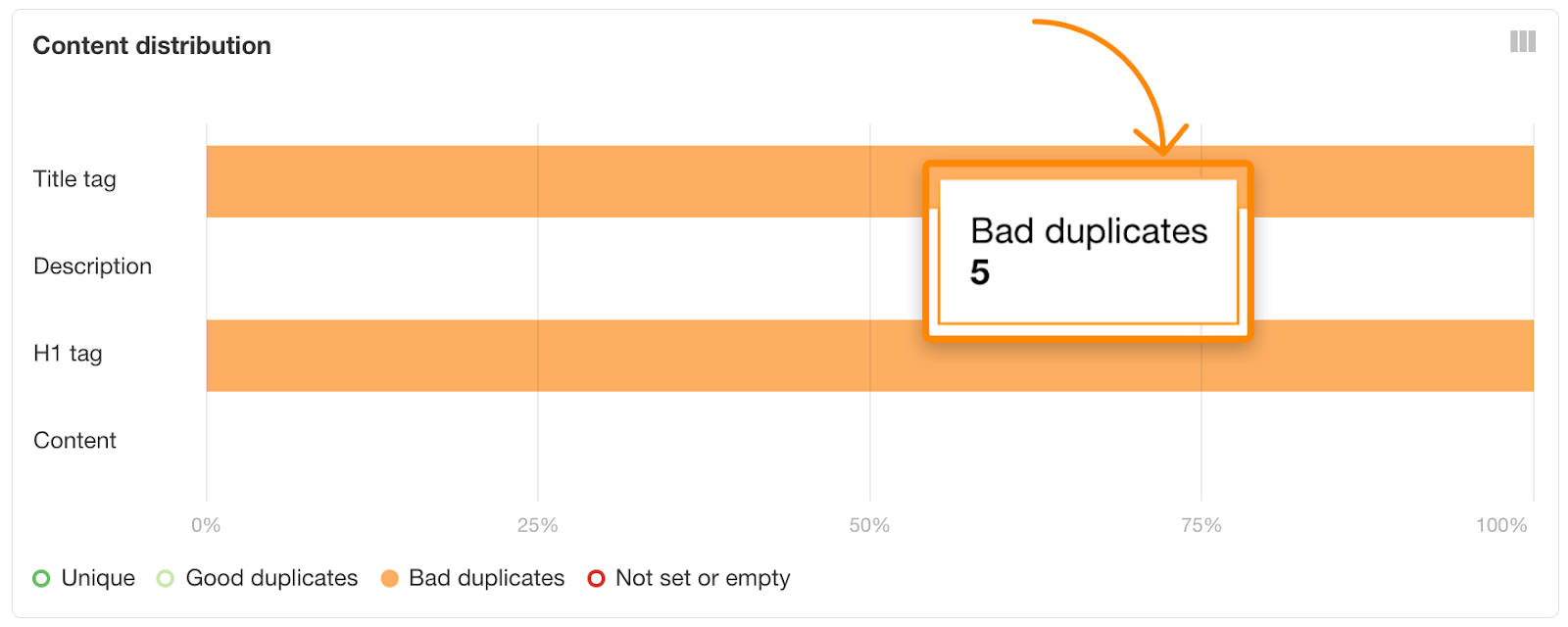
Change the titles of the impacted pages so that they stand out from the others.
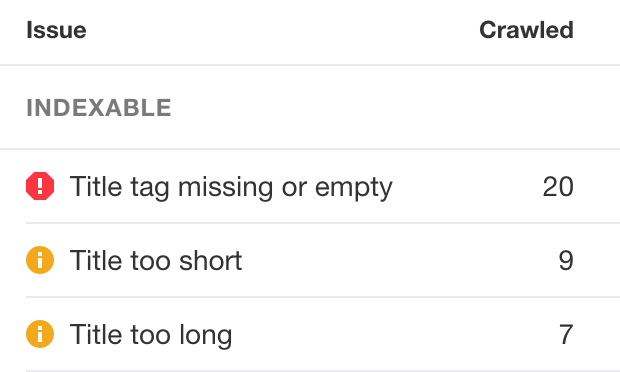
Title tags that are too lengthy, too short, missing, or empty will also be shown in this report.
Meta Description
An overview of the page’s information is provided in the meta description. It’s often used as the summary under search results.
SIDENOTE. Unfortunately, Google isn’t always good at using the meta description you provide. As a matter of fact, they switch to a new clip sometimes.
Just how crucial it is for search engine optimization
As usual, Google has the best explanation:
The purpose of a meta description tag is to provide a concise but informative overview of a page’s content. They operate as a sales pitch, convincing the visitor that this page has all of the information they need.
On the other hand, meta descriptions do not have an immediate impact on search engine rankings. A Google search returns the following results:
The description meta element is used for the snippets we display, but it isn’t included towards our ranking.
Most effective methods
- Include a detailed explanation on each page that you create;
- Exact summarizing of material is encouraged.
- Don’t use vague language;
- Capitalize sentences;
- Make something that people will want to click on, not just anything.
- Respond according to the user’s search intent;
- Always use your keyword where it makes sense;
- Make sure your description is under 160 characters.
How to write a page’s meta description
In the head section of your website, copy the following code:

Yoast makes it simple if you’re using WordPress.
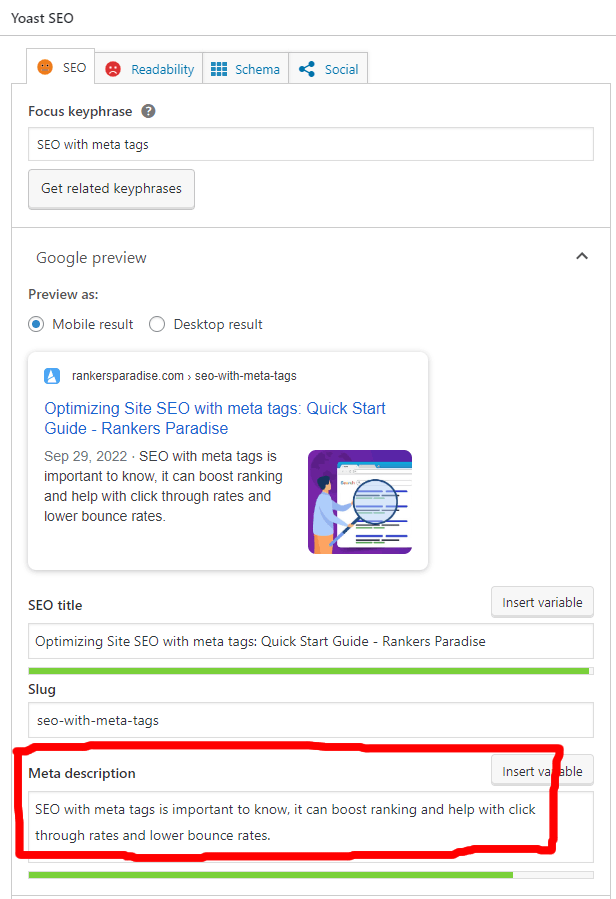
Equal features may be found in other content management systems like Weebly and Strikingly.
Ways to identify and correct typical meta description flaws
Just as with title tags, there are four typical problems with meta descriptions:
- Inappropriate length. According to Google, “the search result snippets are shortened as required, often to match the device width,” therefore there is no hard and fast restriction on meta description length.
- Cannot be found. The search engine advises, “be sure that every page on your site contains a meta description.”
- One page with many meta descriptions. Using many tags at once might cause problems for search engines.
- Meta descriptions that are repeated on many different pages. According to Google’s guidelines, it’s important to “differentiate the descriptions for different pages.”
Use SERPSim or Yoast to check individual pages for the first two issues.
Check for these first three faults on every page of your site by crawling it using Ahrefs’ Site Audit and seeing the On page report.
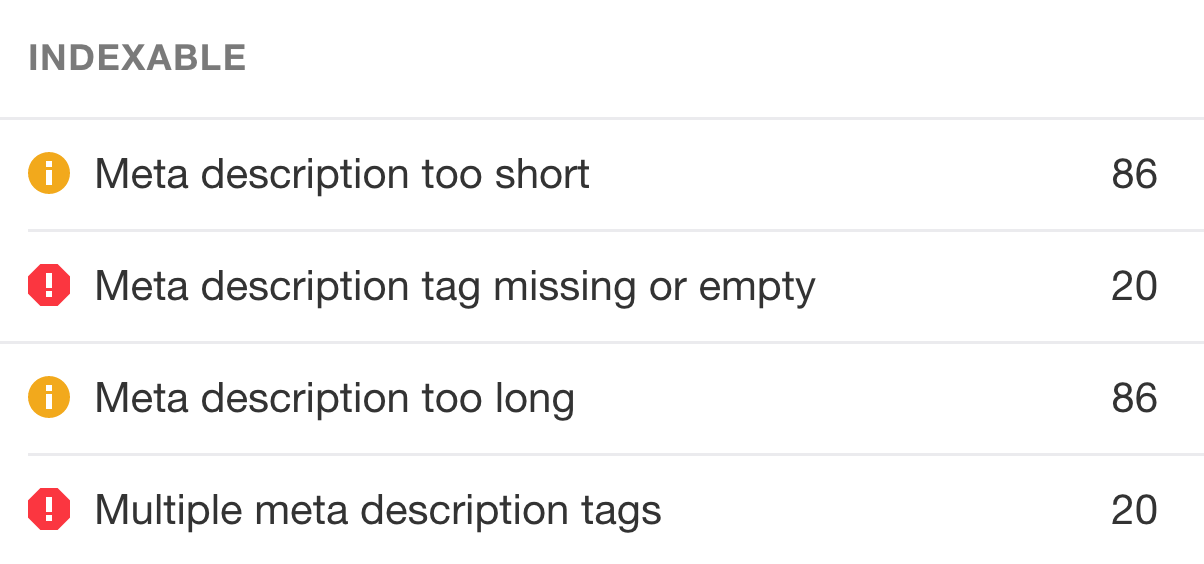
When looking for duplicate meta descriptions, use the Duplicate content report.
To correct this, just replace the description tags as you would normally.
Meta robots
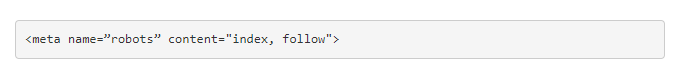
With the use of the meta robots tag, you may specify whether or not you want search engines to crawl your site, and how they should go about doing so.
Syntax
Just how crucial it is for search engine optimization
When used incorrectly, the meta robots tag may have a devastating effect on a website’s visibility in search engines. Learning how to properly use this tag is crucial to your search engine optimization strategies.
In light of it, the following are valid choices for this tag:
- the index command instructs crawlers to collect information from the page;
- noindex: instructs crawlers not to include the page in their index;
- follow: instructs web crawlers to access the page’s associated links;
- nofollow: instructs search engine crawlers to bypass a link since it does not carry any implicit recommendation.
The following are all possible permutations:

To have the same effect as noindex, you can also use the meta name=”robots” content=”none” tag. It is also equal to index, follow if no meta robots tag is specified.
SIDENOTE. Google interprets “nofollow” tags as suggestions rather than mandates. The noarchive, noimageindex, nosnippet, and similar properties are also available. We won’t be covering these more complex numbers here, however, since they are outside the scope of this blog post.
Most effective methods
Only use meta robots tags to limit how Google crawls a page.
Forbidden in robots.txt files are those that include meta robots tags;
Meta Robots Tags: How to Include Them in Your Document
Copy the relevant code from above and put it into your page’s head.
Yoast’s WordPress plug-in allows you to configure meta robots tags in the platform’s advanced settings.
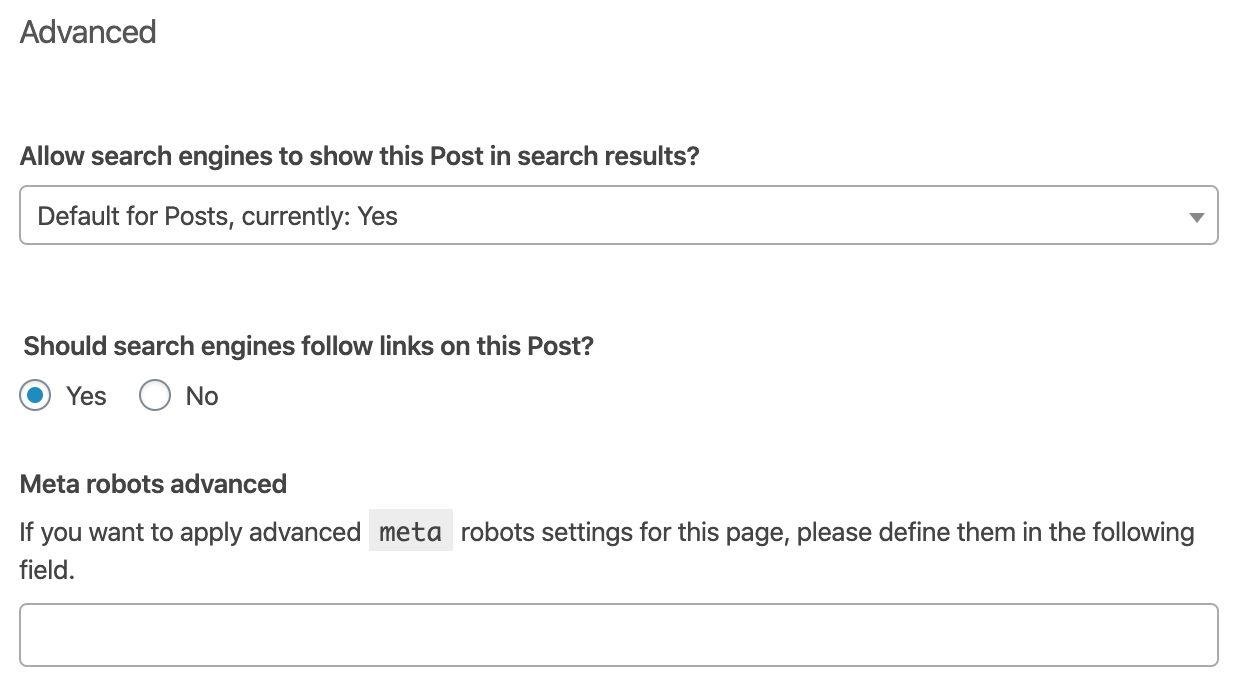
Internally, most content management systems provide equivalent features.
Common problems with meta robots, and how to solve them
Meta robots often make the following three errors:
- Sites with a robots.txt file blocking indexing are effectively invisible to search engines. This hides the noindex robots tag from search engines like Google, so the URL may still be indexed.
- The intruding noindex meta tag must be neutralized. As a result, Google won’t be able to index the page, and so, no organic visitors will be sent there.
- Unauthorized nofollow link in meta description. Without Google being able to crawl the page’s links, potentially valuable material won’t be found and indexed. It also stops PageRank from being passed on to certain sites, which may not be ideal.
With Google Search Console’s Coverage report, you can inspect the first two concerns.
Navigate to the “Valid with warnings” section and check for “Indexed, yet banned by robots.txt” notices to discover indexed sites that may have meta robots noindex settings:
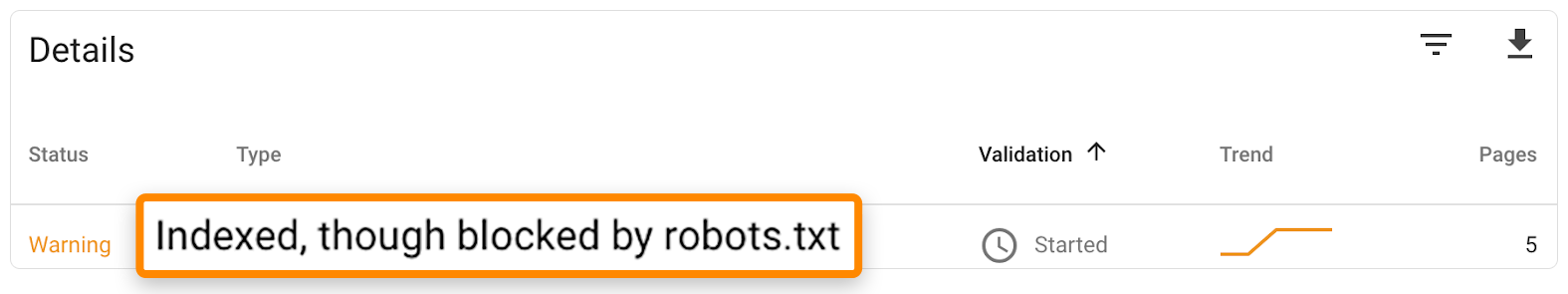
Look for a meta robots noindex tag in the page’s source code. Take off the robots.txt block or the meta robots noindex tag, as appropriate for your goals.
Click the “Excluded” tab and check for pages “Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag” to identify missing meta robots noindex tags:
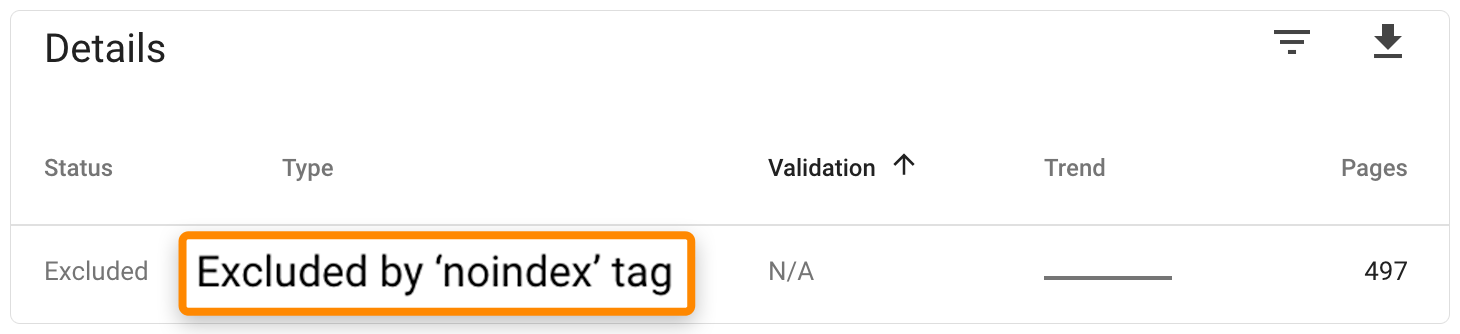
In order for pages to be indexed, the robots meta tag must be removed.
Crawling the site using Ahrefs’ Site Audit and looking for “Nofollow page” warnings in the Indexability report can help you locate pages with rogue meta robots nofollow tags.
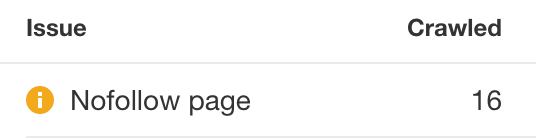
If you don’t want search engines to index the page’s links, remove the tag.
SIDENOTE. A few concerns, include pages with noindex tags in your sitemap, are left unaddressed here. The Indexability report in Ahrefs’ Site Audit may provide light on these concerns.
Meta viewport
Meta viewport tags define the viewable region of a web page. It tells the browser how to display the website depending on the device being used.
Just how crucial it is for search engine optimization
According to Google, “the existence of this tag signals to Google that the website is mobile-friendly,” and as of 2015, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly web pages in mobile search results.
Here’s an example of what a page may look like on a mobile device with and without the use of a meta viewport tag:
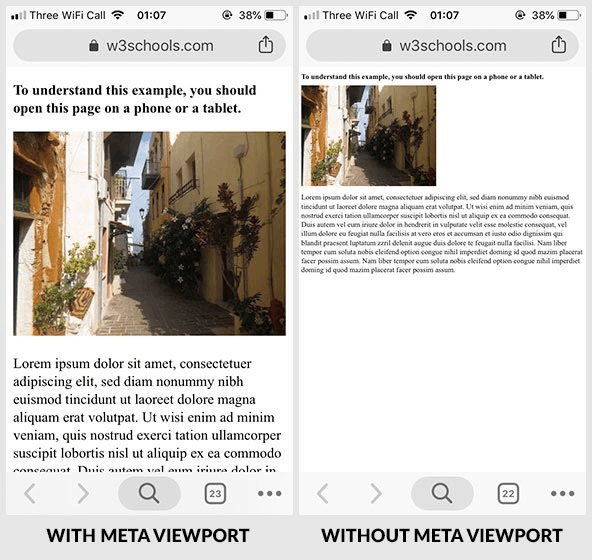
When a mobile site loads the desktop version instead, many consumers will likely close the browser. It’s distracting, and it makes the text difficult to read. As a result, Google may interpret these signals as an indication of a problem with your site.
SIDENOTE. A mobile-friendly website requires more than just the viewport tag. A mobile-friendly layout is essential for any website.
Most effective methods
- Include the meta viewport tag on all of your webpages;
- If you aren’t sure what you’re doing, just use the “standard” tag (see below)
Instructions for including a meta viewport tag on your page
Just copy this code into your website’s head:

Viewport meta data should read “width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0.”
It’s important to remember that the content property doesn’t have to be set to width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, but that this is the most common implementation and the right one for most sites.
Understanding frequent meta viewport errors and how to correct them
Tag-related difficulties are unusual on current websites since most CMS’s and themes change the viewport automatically.
However, you may use the Mobile Usability report in Google Search Console to examine your site for problems.
Pages with usability difficulties on mobile devices are shown here. There will be a “Viewport not set” error if the absence of a viewport meta tag is even partially to blame for this problem.

Add the proper meta viewport tag to the pages that are having this problem.
IMPORTANT
Problems with mobile display that originate in CSS styles that aren’t responsive will persist even after adding a meta viewport tag. A developer should be consulted if the addition of a meta viewport tag does not resolve the issue.
What, you’re not using Google’s Search Console?
Meta viewport is often configured at the domain level and is often hardcoded into the theme.
Examine whether or not your homepage makes use of a meta viewport element using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
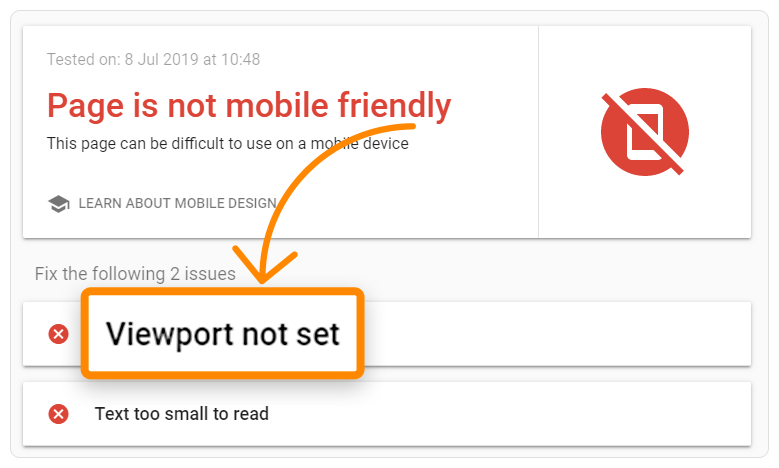
The tag probably isn’t used anywhere else on your site if it isn’t already on your homepage.
It’s important to keep in mind that this is by no means a failsafe strategy, and that Google Search Console should always be used if at all feasible.
Meta charset
The page’s character encoding may be changed using the meta charset element. Simply said, it specifies how the text on your web page should appear to the user’s browser.
There are several character sets, however the two most widely used on the internet are:
- The Unicode Text Encoding (UTF-8)
- Coding for the Latin alphabet (ISO-8859-1).
Check out the entire list here.
Just how crucial it is for search engine optimization
If you choose the improper character encoding, certain characters may seem garbled in the browser.

User experience is negatively impacted by incorrect character formatting, which may make your websites seem broken.
Possible negative effects on search engine optimization include:
- The absence of links to your site from other sources.
- Low engagement metrics, including page views and time spent.
- Your material isn’t being indexed by search engines.
Still, let’s face facts:
Unless your page is seriously damaged due to charset concerns, which is quite uncommon, the effect will be fairly modest.
In any case, it’s worth mentioning that Unicode/UTF-8 is Google’s preferred encoding format.
Most effective methods
- Please include the meta charset tag in all of your websites;
- To the extent practicable, UTF-8 should be used;
- The HTML version you’re working on has to have proper syntax (see below).
Web page meta charset tags and how to use them
Just copy this code into your website’s head:

In order to ensure proper display of characters, this page has been coded using the UTF-8 character encoding.
Use this code instead if you’re using HTML5 or a lower version:

Check your source code if you don’t know which version of HTML you’re using.
code>doctype html> Simply said, if you can see this, you’re utilizing HTML5.
Common errors in meta charset and how to repair them
Character encodings like UTF-8 and ISO-8859-1 are widely used on webpages.
The former option is far better than the latter.
That’s why it’s important to make sure all of your website’s pages are encoded in UTF-8. Ahrefs’s Site Audit provides this functionality. Just adjust them in the Page Explorer:
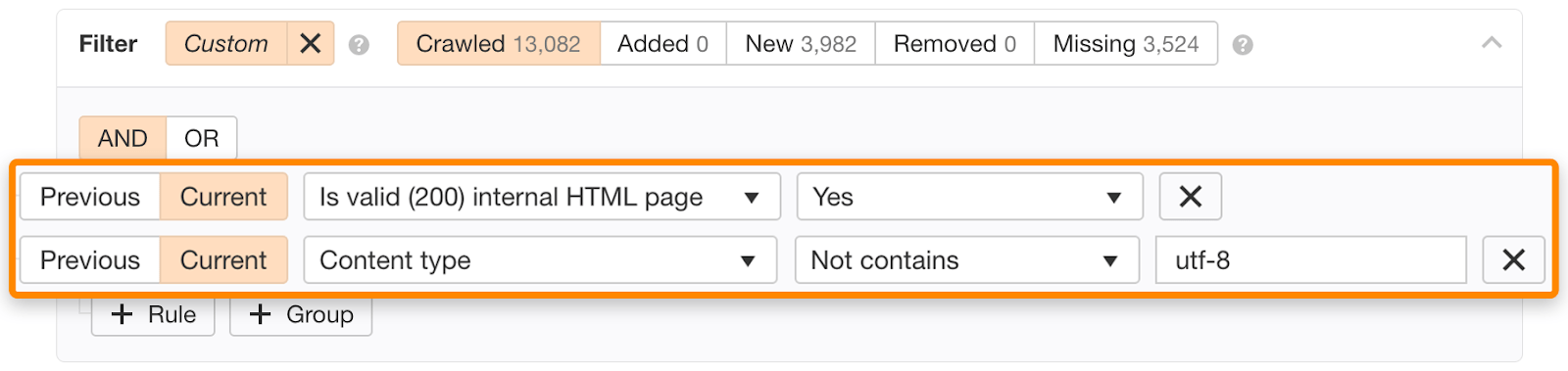
Manually inspect each result for any character encoding problems if the search returns any results.
If you have the option, switch to UTF-8 encoding. That could work, but I wouldn’t count on it. However, if you don’t include a meta charset, the user’s browser will likely make an educated estimate and display unexpected characters instead.
Meta-refresh redirect
After a certain length of time, a user may be sent to a new URL using a meta refresh element in their web browser.
Just how crucial it is for search engine optimization
For the sake of your SEO, you should avoid using meta refresh redirect tags, despite the fact that Google recognizes and appreciates them.
Several factors contribute to this:
- Currently unsupported by several browsers;
- Sometimes causes user confusion (and security issues);
- It takes some time for the page to be parsed before the target URL is seen.
According to a tweet from Google’s John Mueller, another possible problem occurs when there is no canonical tag on the page.
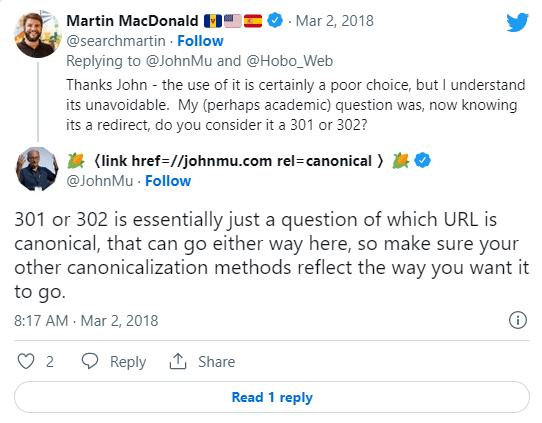
Most effective methods
- Redirect tags in meta refresh should be avoided unless absolutely essential.
- Instead, try a 301 redirect.
The correct way to implement a page-wide meta refresh redirect tag (if you really need to)
In the head section of your website, copy the following code:

A delay in seconds may be set with the content property, and the redirect URL can be set with the URL attribute.
Finding and fixing typical errors in meta refresh redirects
The use of meta refresh redirects is discouraged and should be avoided.
Look in the Internal Pages report of Ahrefs’ Site Audit for the “Meta refresh redirect” issue to locate these broken links.

To the extent practicable, change them to redirections of type 301 or 302.
If there isn’t one, you should add one so that the “canonical” tag always points to the “master” copy of the page.
So, think about Meta Keywords?
While it may seem like a good idea to provide a list of keywords in the meta keywords element, Google hasn’t taken this into account for rankings since 2009.
[…] keyword meta tags rapidly became a place to dump often-irrelevant phrases without the ordinary visitor ever seeing them; as a result, Google stopped discarding the keywords meta tag many years ago. If yours are overstuffed with keywords, it might hurt you in Bing’s search results since the search engine declared in 2011 that it uses the tag as a spam indication.
To be on the safe side, get rid of the meta keywords tags altogether.
To achieve this, you need do a site crawl using Ahrefs’ Site Audit and then enter the following parameters into Page Explorer:
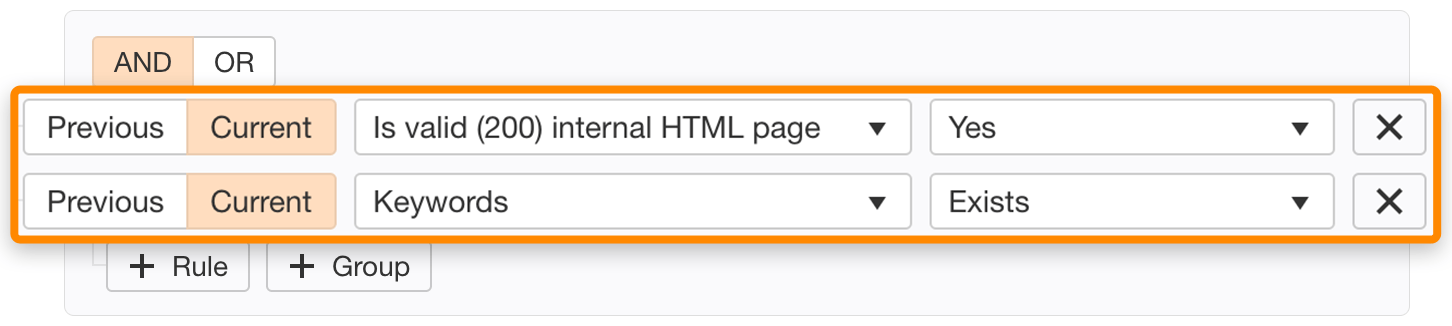
If a page’s meta keywords tag is present, remove it.
It’s important to remember that, in most cases, deleting these tags is simple, since many websites establish a sitewide meta keywords tag in their CMS, and erasing the tag from all pages only entails erasing that one line of code.
In conclusion
The following six meta tags are all you need to know to avoid making any major SEO mistakes; meta tags aren’t difficult to understand.
If you want to know more about meta tags, this article can help you.
If you want more people to visit your site through social media, you should learn about the Open Graph meta tags.
Keep learning SEO:
How to add keywords to your website for google search
A Starter Guide to SEO – Boost Ranks and Traffic with Search Engine Optimization