For the top keyword positions, you put in a lot of effort. But there’s still a lot of work to be done. It’s unlikely that your website will get many hits if your listing doesn’t convey value. Every missed chance to connect with your audience costs you a significant amount of money.
Optimizing your CTR is a search marketing strategy that isn’t given enough credit. This can have a HUGE effect on your total traffic.
Throughout this post, you’ll find out more about the click-through rate and the nine proven ways to increase it.
Before we get started, let’s make sure we’re all on the same page about what CTR is, why it’s essential, and how high your CTR should be.
Definition of click through rate
The connection between the number of clicks on your link (clicks) and the number of times your listing appears on a SERP is known as the click-through rate (CTR) (impressions).
Using CTR (click-through rate) as an indicator, you may see how well your search engine ad is doing.

A 5% CTR indicates that out of every 100 individuals who see your website, 5 of them will click through to it.
Why is CTR so important?
It goes without saying that a higher CTR means more traffic to your website. This works on Ads and in the organic search results pages.
We appreciate visitors to our website since it means they’re one step closer to becoming paying clients.
In terms of strategy, the CTR is also valuable. It may be used to estimate the amount of traffic that organic search improvements will bring and to prioritize content enhancement.
What is the average CTR?
While determining whether or not your CTR is excellent, you may wonder what an average CTR is.
Based on SERP rankings, the average CTR for 17 billion terms was calculated in research conducted in 2021.
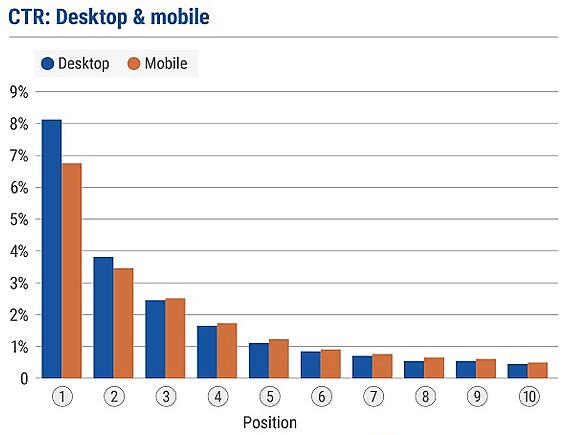
SeoClarity’s average desktop and mobile click-through rate
This graph may make you think your site is a long way behind or that your site is doing well and you can stop right here—but stick with me.
Using a broad benchmark to compare your site’s CTR against isn’t very useful since it varies greatly from industry to industry. If you’re interested in learning more, you can see the whole study, which has statistics for 13 different sectors.
Even while you may use the average click-through rate (CTR) as a guide, it’s best to dive deeper into your website’s analytics to see whether your benchmark needs to be adjusted.
What pages should I optimize for click-through rate (CTR)?
In the same way, you don’t want to optimize for CTR as a site-wide activity, and you don’t want to look at CTR from a wide angle.
When it comes to CTR optimization, you may have heard marketers talk about locating the “low-hanging fruit.”
Sign into Google Search Console, choose your search property, and view the Performance > Search Results report to see which sites to improve for CTR.
The date range will be set to the past three months by default. You can, however, change the time depending on how busy your site is and what time of year it is.
From the drop-down menu, select only “total impressions,” “average CTR,” and “average position.”
By clicking on the “+” symbol with the phrase “New,” you may add criteria to narrow your search to a certain country (and content subject).
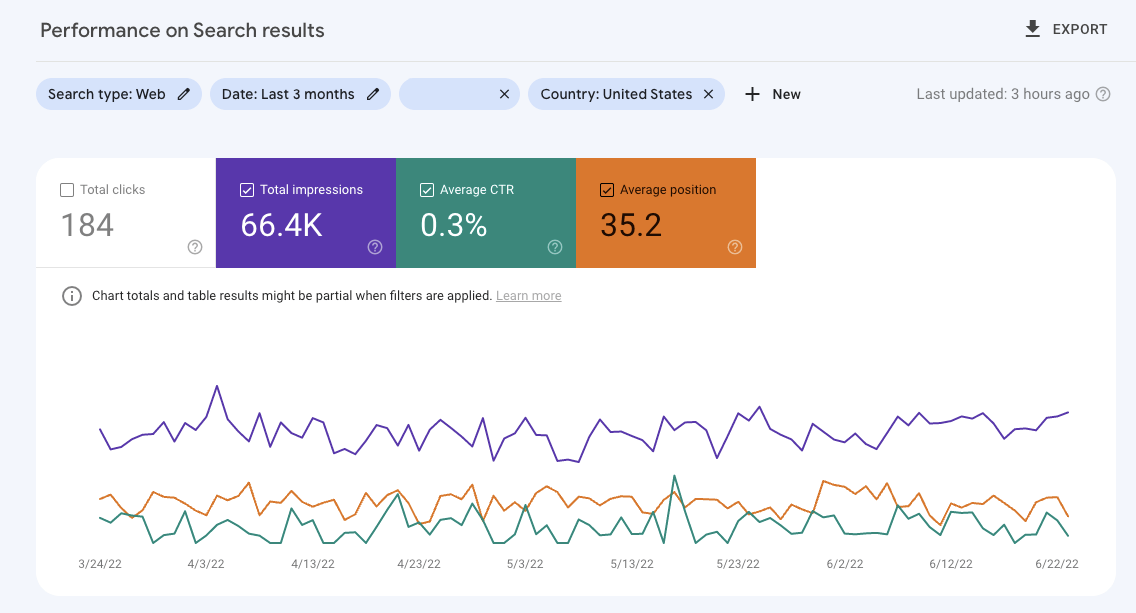
This screenshot shows GSC filtered by country and omitting non-branded inquiries.
Once you’ve risen to the top of the first page—possibly inside the first five search results—it’s time to start thinking about CTR optimization.
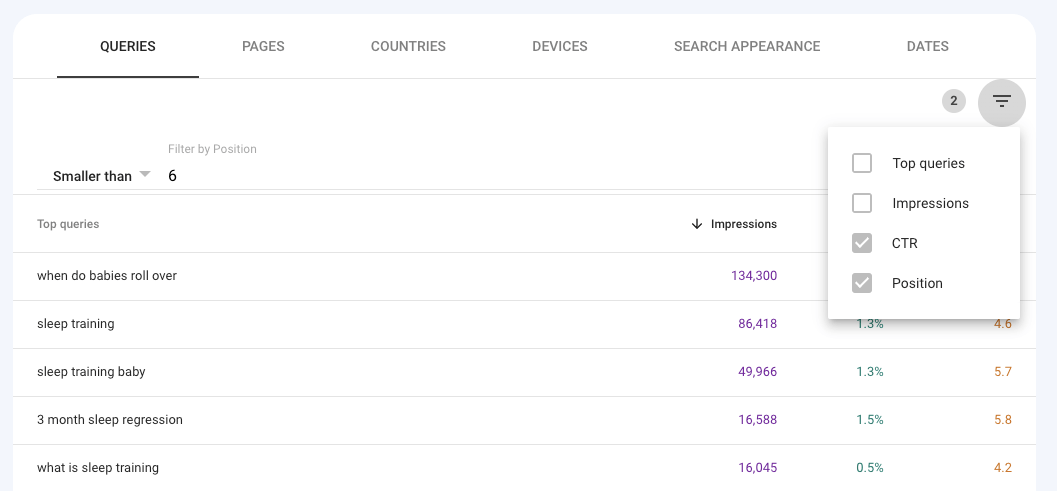
Your data may be segmented by “position smaller than 6” and “CTR less than (enter your average CTR here)” by clicking the three lines in the top-right corner of your search console table.
In the picture above, for example, I chose to segment by target country, get rid of brand name searches, filter by top rank positions, and sort by impressions to find the site’s most popular searches.
Consider the following questions with regard to your company’s goals when looking at this table. You’re on the lookout for a popular trend or a useful term that can help promote your company.
“Sleep training” is a nice example of a search term that has a high search volume and an average position in the top five. CTR, on the other hand, is a mere 1.3%.
Next, we’ll look at search traffic and click-through data trends. Using Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer makes this process a breeze:
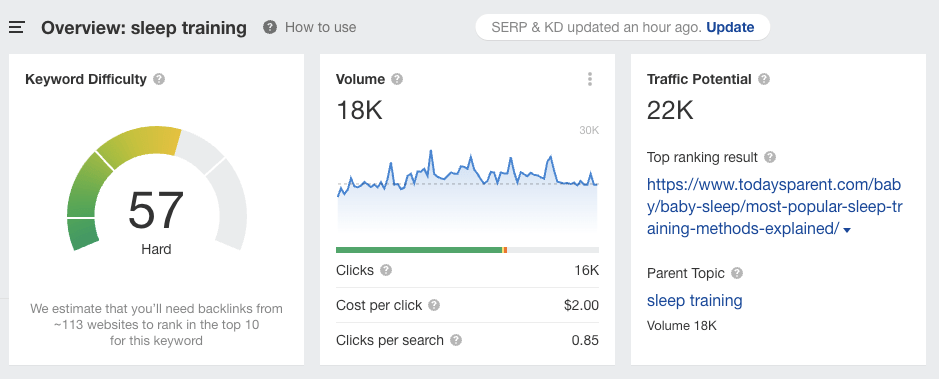
Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer provides an overview of the keyword “sleep training.”
We want to see an increase in search volume and an increase in the number of people clicking on organic results (click distribution).
A page that gets very few organic hits isn’t worth the effort.
Search volume for “sleep training” has remained steady, with roughly 63% of all clicks going to organic results instead of paid ones.
If we spend more time and money on raising the CTR, we can expect the value of this page’s traffic to go up.
The following are suggestions for increasing click-through rates (CTR).
We’ve learnt that a high search engine rating doesn’t ensure that people will actually visit your site. It needs greater skill.
A site with a CTR of 1.2 percent appears in the top five results for a high-value search query.
Follow these next suggestions if your page is on the first page but the CTR is lower than intended.
Your H1 tag’s title tag should match your META DATA title tag.
According to Ahrefs’ assessment of 953,276 sites, Google rewrites title tags 33.4 percent of the time.
The research also showed that if your META DATA title tag matches the page’s H1 tag, Google is less likely to alter it in search results.
This little nugget of wisdom is quite easy to implement. When it comes to SEO, it’s better if the page title and H1 tag match the content of the article itself.
Ahrefs’ Site Audit’s Page Explorer tool may show you whether or not your titles are being rewritten and whether or not they match your H1 tags.
To do this, follow along with the steps provided below.
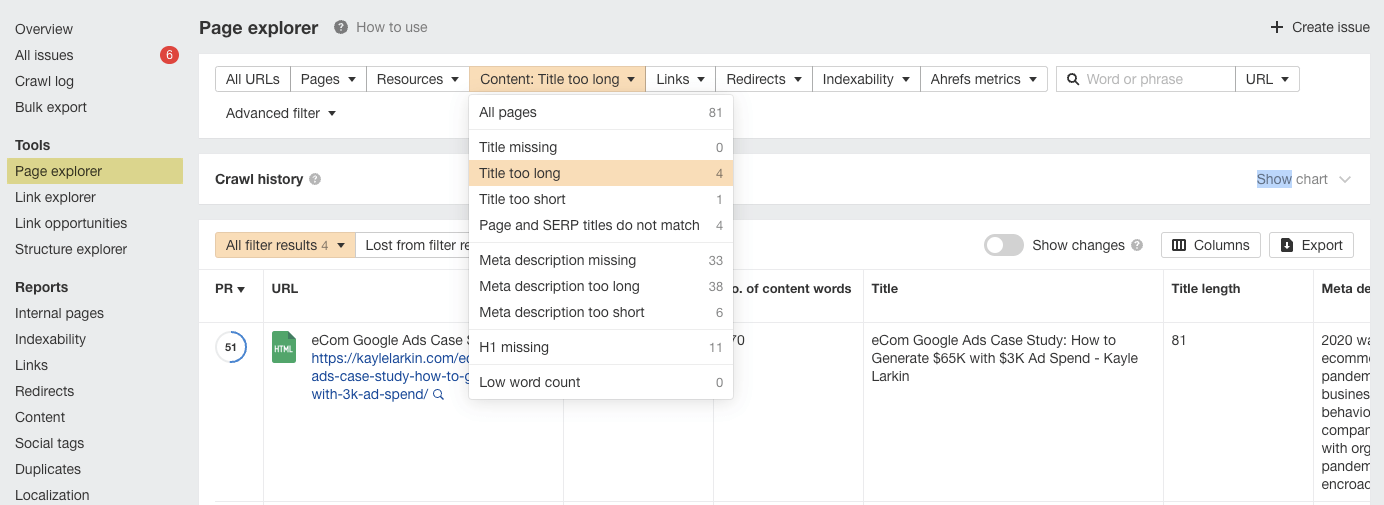
Go to the Page Explorer report in Site Audit. Select “Content” and then “Page and SERP titles do not match” from the drop-down menu.
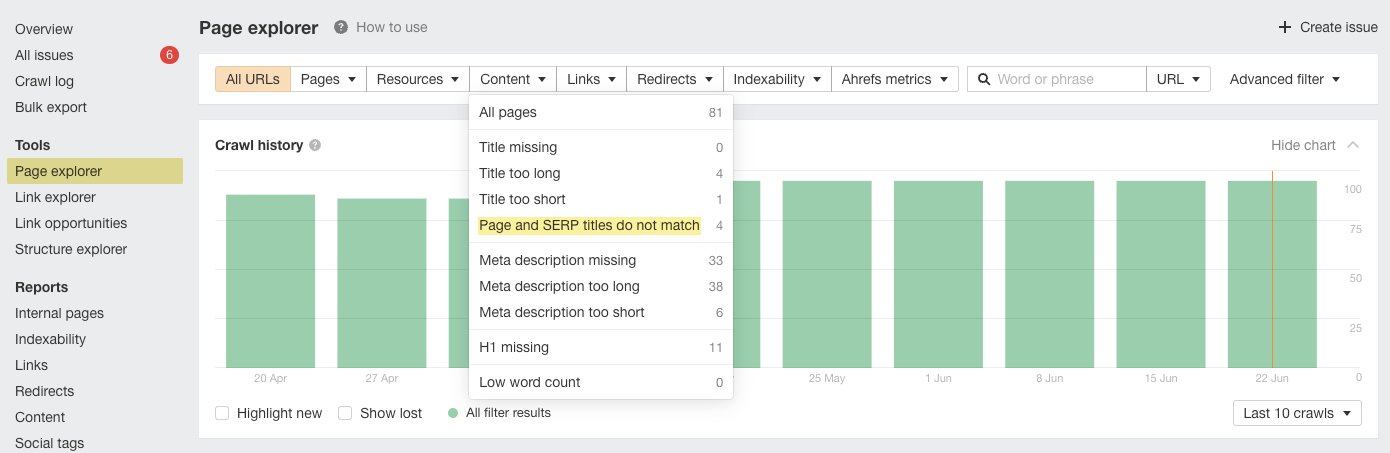
For “Page and SERP titles do not match,” Ahrefs’ Page Explorer report filter has a screenshot of the filter.
Pages whose titles don’t match the SERP titles will be included in a table instead. Right-click “Columns” in the top-right of that table.
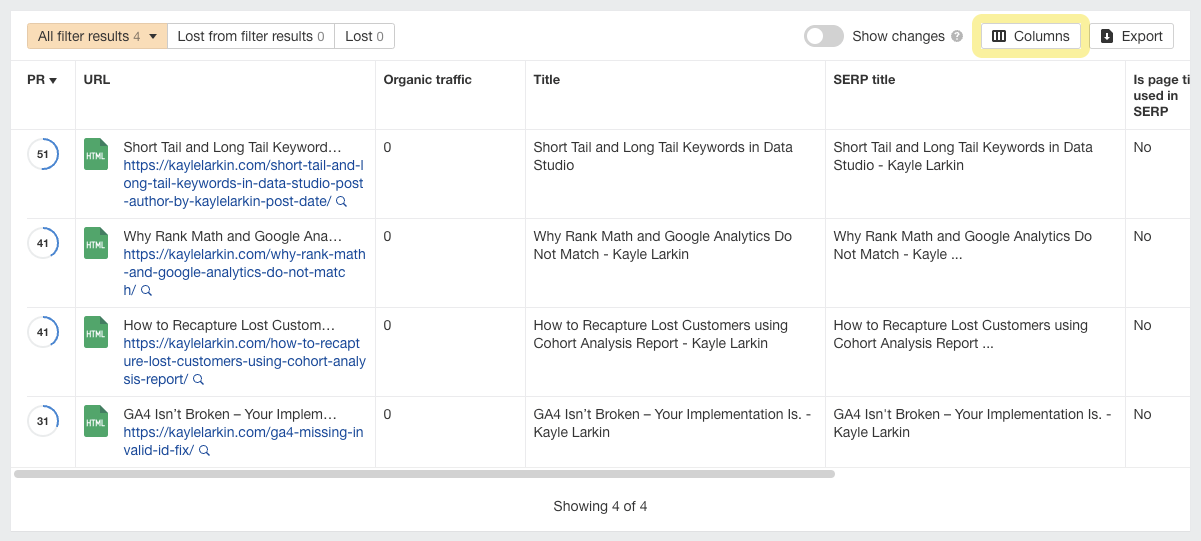
Editing columns in the Ahrefs page explorer report
Open “Content” from the left-hand menu and choose “H1.” The “H1” widget may be dragged and dropped after the SERP title. Then click “Apply.”
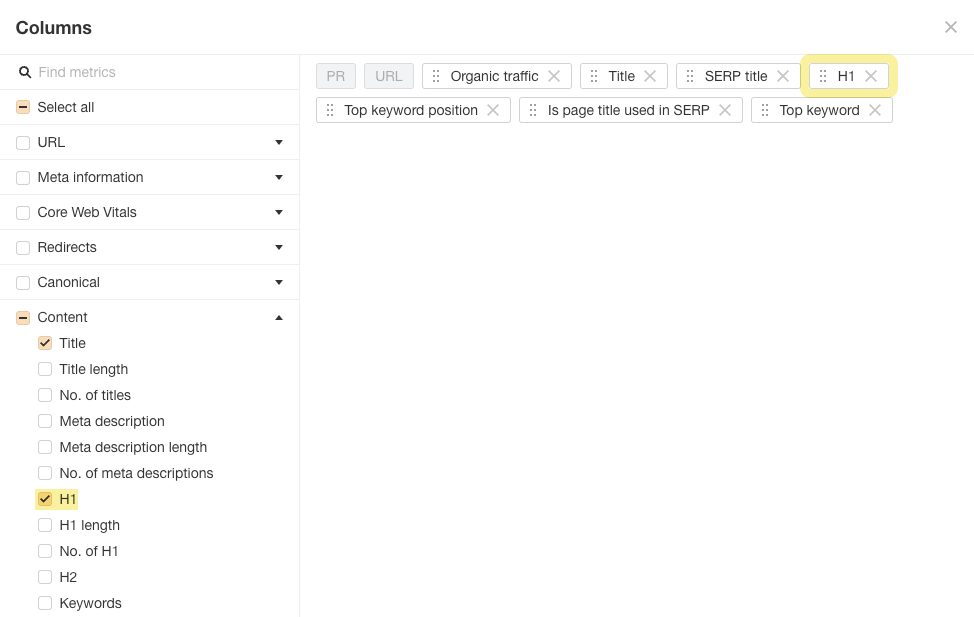
Adding columns to Ahrefs’ Page Explorer report is seen in this screenshot.
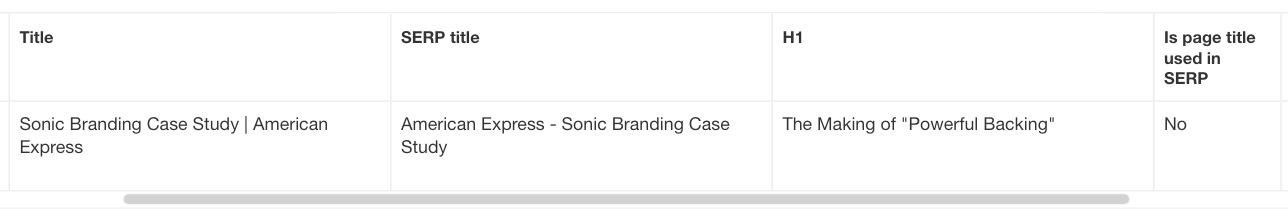
Using this information, you can check whether there are any H1s or title tags that may be improved.
The Page explorer report screenshot from Ahrefs shows the title, SERP title, and H1 mismatches.
The second step is to come up with eye-catching headlines (not clickbait).
Because clickbait is becoming more common (hyperbolic titles that draw readers’ attention to questionable information), it’s more important than ever to come up with titles that accurately describe what your site is about.
As long as it’s done respectfully, it’s OK to draw the reader’s attention with a title. We all know how quickly the confidence of a reader may be eroded.
Avoid getting chopped off because of the pixel length.
Page names shouldn’t be longer than 580 pixels (about 50–60 characters) so that they don’t get cut off in search engine results.
Your page titles will be legible on desktop and mobile devices if they are this long.
Ahrefs’ Site Audit makes it easy to locate the problematic pages. Navigate to the Page Explorer app. Choose “Title too lengthy” from the “Content” drop-down filter.
Ahrefs Page Explorer screenshot showing the “Title too lengthy” error.
When developing new pages, make use of a SERP preview tool to see how your title and description will appear in search results.
Align with the goal of the search (know why).
The purpose of a search is explained by the searcher’s aim. Why did this person look for this information? Do they know what they’re looking for?
As the first thing visitors see, your search listing ought to convey how your website properly fulfills the user’s inquiry.
It is possible to change our titles and write meta descriptions so that the whole SERP snippet fits with what the searcher was looking for.
When you examine the term in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer and click down to the SERP overview, you may get a sense of what people are searching for.
A screenshot of the SERP overview in Keywords Explorer for Ahrefs.com.
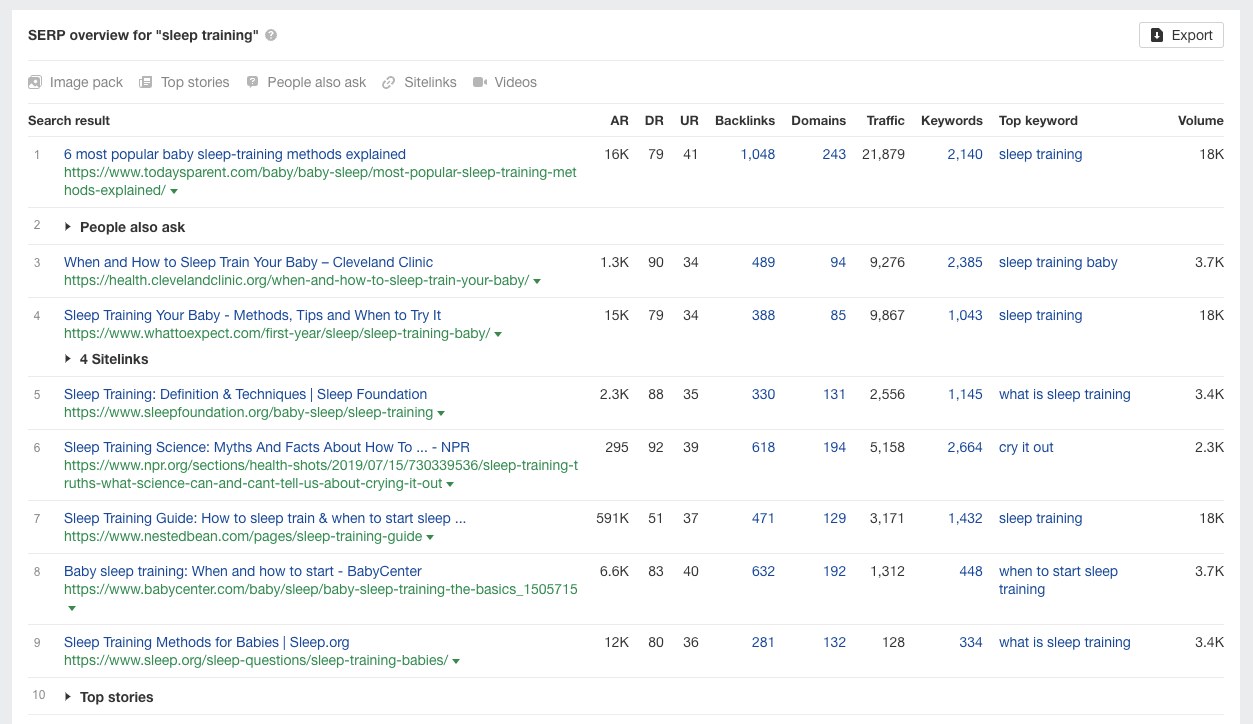
A look at the top keywords and search results for “sleep training” tells us that people want to know what it is, when, and how they may start.
The phrase “sleep training” isn’t click-worthy, but we may go a step further and add, “Sleep training Your Baby: When and How to Start.”
Clearly state what distinguishes your material from the crowd.
Is there a compelling reason for a user to click on your content rather than the other results that are right in front of them?
The breadth of coverage or the simplicity, freshness, or the brand’s reputation as a subject matter expert may be the answer to this question.
If you have a technical task that takes a lot of time or seems hard, talk about how the article makes it easier.
“Baby Sleep Training for Beginners: A Step-by-Step Guide” might be an appropriate title.
For data that has to be current, such as poll results, you may provide the month and year of the study’s completion as a descriptor. For instance, “Baby Sleep Training Methods Popular in 2022.”
Use a well-known brand name as a keyword wherever possible. There is a sense of familiarity and trust that comes with brands.
According to a SERP analysis, “cry it out” is a well-known sleep-training technique.
The term “Sleep Training Methods: When Cry It Out Isn’t Working” could be a good starting point, and we can elaborate on it in the meta description.
Don’t follow the herd (counter-narrative)
Bring an alternative viewpoint to bear on a generally accepted notion or norm.
As a result, readers are automatically drawn in and eager to learn more.
How to Sleep Train Your Baby (The Gentle Way) or “A Modern Family Guide to Sleep Training (Tears Free”) are two examples of books that explain how to do it.
Cry it out was our top term in our SERP review, and both titles take a different tack on the story.
In brackets, add an additional advantage (draw the eye).
You may attract attention to an additional advantage by using brackets or parenthesis in your title. An example is “How to Sleep Train a Baby (And Save Your Sanity.)”
Use a number instead of a letter (readers love lists).
The reader will know you’re providing them with a list if your headlines include numbers. People also like lists because they show that the information is well-organized and makes sense.
“Sleep Training” is transformed into “5 Baby Sleep Training Tips for a Better Night’s Sleep.”
Make use of schema markup to get more detailed results (provide more information).
Okay, so this isn’t a meta description or a title tag. However, it is a proven and effective method of raising CTR.
This kind of search result is called “rich” if it has extra information based on how the data is organized.
Schema markup may be used to show extra information, such as the price, reviews, or cooking times, on your website. It helps to increase the number of clicks since it gives prospective purchasers more details they care about.
A high review rating, for example, may encourage more people to click on a search result that appears in the top results.
A rich SERP result from Google may be seen in the image below.
In closing, these are my last thoughts.
If your site’s click-through rate has stagnated, use the strategies suggested above to kickstart it.
It may take some effort to identify and address “low-hanging fruit,” but it does not have to be laborious. Using Google Search Console and Ahrefs can help you simplify your workflow.
Keep learning SEO
Off page SEO checklist guide to the top
What is meant by backlinks in SEO?
Tools that will make you the best backlink builder